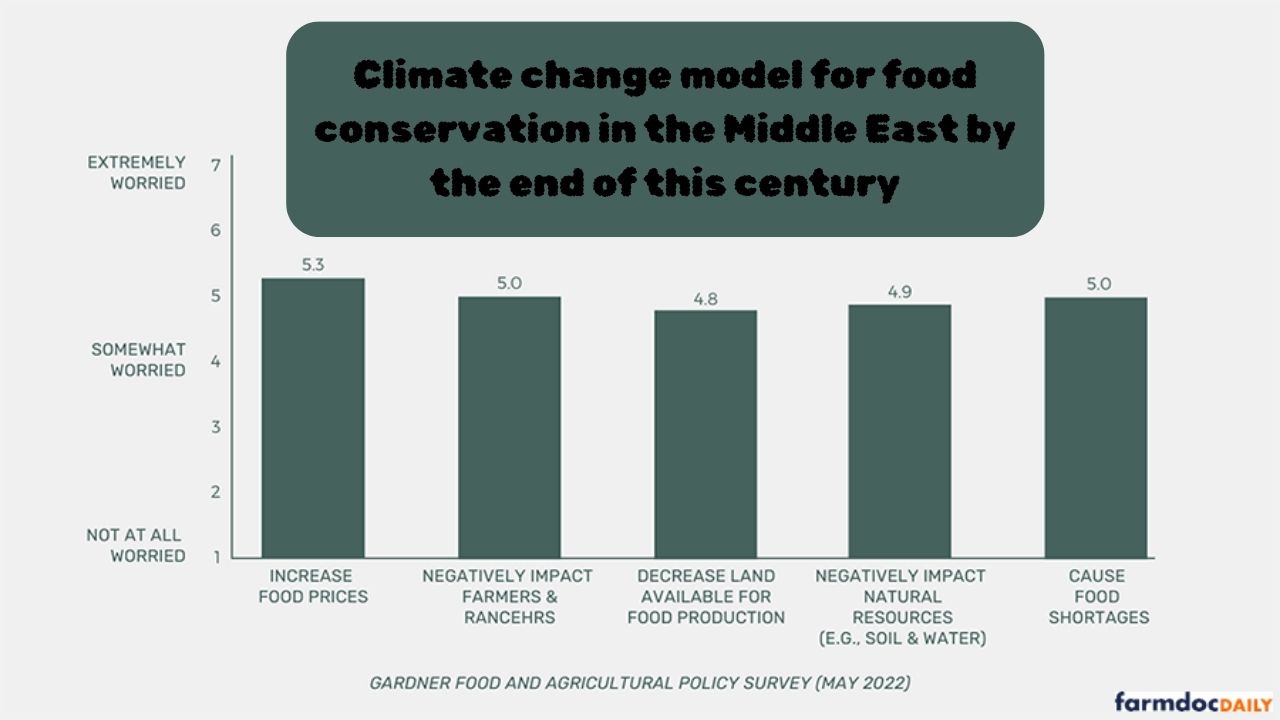
The Climate Change Model for Food Security in the Middle East by the End of the Century is a tool that predicts how climate change will affect crops and food supplies. It uses data such as temperature, rainfall, soil quality, and water availability. The model helps farmers and policymakers plan how to save food and grow crops in the future.
The Middle East is experiencing extreme heat, drought, and water scarcity. These problems can lead to food shortages. Imagine fields drying up and crops failing. Without action, people could face food shortages by 2100.
The model predicts which crops will survive and where to plant them. It helps improve irrigation and manage water use wisely. Governments can use it to develop food plans. It guides farmers in adapting to a changing climate.
Understanding Climate Change Impact on Middle Eastern Agriculture
Climate change poses a major threat to agriculture in the Middle East. Extreme heat, water scarcity, drought, and soil degradation are reducing crop yields. Key crops such as wheat and dates are being affected.
Farmers are finding it increasingly difficult to survive, and food shortages are increasing. Drought-tolerant crops must be planted to save water in the region. Proper water management and modern irrigation methods are essential.
Developing a Climate Change Model for Food Conservation
Climate change poses a major threat to agriculture in the Middle East. Extreme heat, water scarcity, drought, and soil degradation are reducing crop yields. Key crops such as wheat and dates are being affected.
Farmers are finding it increasingly difficult to survive, and food shortages are increasing. Drought-tolerant crops must be planted to save water in the region. Proper water management and modern irrigation methods are essential.
Strategies to Ensure Food Conservation in the Middle East
Various approaches are being used to achieve food security in the Middle East. Such perspectives focus on selection manufacturing, food storage, waste reduction, and policy development.
- Production and agriculture: transplant drought-tolerant crops, using present irrigation methods such as drop irrigation, and grow yields between hydroponics or vertical farming.
- Supply chain and storage: fix grain reserves with Present technology, creating strategic stocks, and enhance food delivery.
- Waste reduction and utilization: finish food useless, inform buyers, and distribute surplus food through food banks.
- Policy and regional cooperation: generate clear policies, provide financial support, increase cooperation between government and farmers, and develop food monitoring systems in the region.
The Future of Food Security by 2100
By 2100, the planet will feature major challenges in food security. The population will reach almost 10 billion. Extreme heat, drought, and climate change will damage crops.
Current technology and structured agriculture must be used to expand food production. decreasing food waste and confirming access to healthy food for all is essential. Great policies and support for farmers will build up food security in the future.
Conclusion
Weather change and water scarcity in the Middle East are experience a major impact on food production and the livelihoods of farmers. Future food security will require innovative models, drought-tolerant crops, advanced irrigation, and the use of technology.
Strengthening food supply chains, reducing food waste, creating better policies, and increasing regional cooperation are also important. If these measures are taken, the region will be able to achieve food security, sustainable production, and access to food for all by 2100.