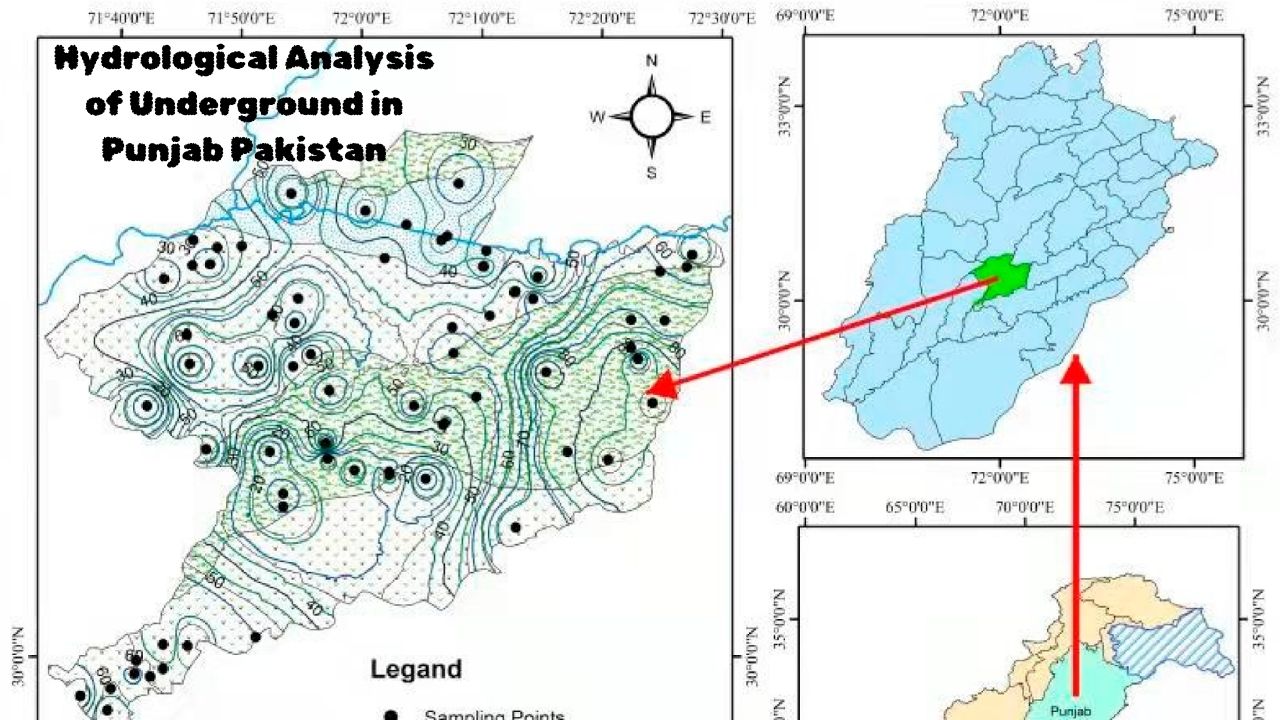
The groundwater analysis of Punjab reveals a worrying reality. Excessive water extraction for agricultural needs has disrupted the water balance. In many areas, water levels are rapidly declining and salinity and pollution have affected the quality, making irrigation difficult.
Research studies are using modeling, GIS mapping and geophysical methods to better understand the quantity and quality of water. The results show that the risks are higher in central and southern Punjab. Effective management, restoration of water bodies and integrated strategies have become the need of the hour.
Understanding Underground Water Systems in Punjab Pakistan
The groundwater system of Punjab is like a large natural reservoir that is spread under the ground. This water mostly seeps into the ground from the Indus River and irrigates the fields. Farmers depend on this water. But when more water is extracted than necessary, the water under the ground starts to decrease.
Today, the problem is that the water that is coming out is not coming back as much. Due to this, the motors have to be installed deeper and the cost also increases. Salt water is also coming up, which is harmful to the crops. Therefore, it is necessary to use both the water above and below the ground wisely.
What Is Underground Hydrology and Why It Matters
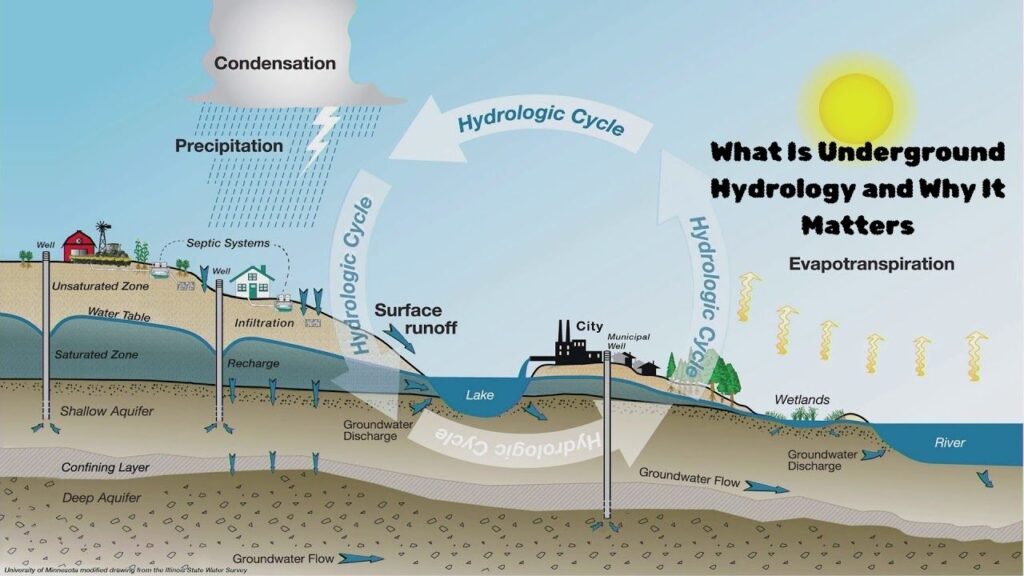
In simple terms, groundwater is the water channels and reservoirs beneath the soil. This knowledge tells us how rain or river water seeps into the ground and then where it slowly flows. This water travels between soil and rocks. This knowledge is important because it is the water we use for drinking, farming, and daily activities. If we don’t understand it, this precious water can go to waste.
Geological and Climatic Factors Affecting Underground Water in Punjab
In Punjab, groundwater is affected by both the soil structure and the weather. The soil here is mostly made up of sand, clay and silt, which holds water. Rain and monsoon water is absorbed into this soil. But when there is less rain or the temperature increases, less water is produced. Taking too much water brings up salty and polluted water, which poses a threat to the future.
Methods Used for Hydrological Analysis of Underground in Punjab Pakistan
In Punjab, Pakistan, scientists study underground water in different ways to understand how much water is there, its quality, and where it is stored. These methods help to see how water moves under the ground, where it is safe to use, and where there might be problems like too much salt.
Main Methods:
Geophysical Methods:
- Electrical Resistivity Surveys (ERS): Maps layers under the ground (soil, sand, water) and checks water quality.
Hydrogeological Investigations:
- Observation Wells & Data Collection: Watch water levels and take samples.
- Lithological Analysis: Understand ground layers using ERS and borehole data.
- Water Quality Sampling: Test water before and after rainy seasons to see if it’s safe.
GIS & Spatial Analysis:
- Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW): Make maps showing water quality and salt levels.
- Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) & Frequency Ratio (FR): Find good places for water storage and areas at risk.
Groundwater Modeling:
- MODFLOW: Predict how groundwater moves and future water levels.
- Machine Learning (XGBoost, etc.): Study local water changes more accurately.
Statistical Analysis:
- Correlation Analysis: Check relationships between chemicals in water.
Main Goals:
- Find safe areas to extract water.
- Map fresh and salty water zones.
- Check groundwater storage and recharge areas.
- Monitor water levels and storage changes.
- Make plans to manage water sustainably.
Groundwater Quality Assessment in Punjab Pakistan

There are several serious problems in groundwater quality in Punjab, Pakistan. Most of the water in PPPs contains salts, arsenic, iron, nitrates and bacteria, making it safe for large-scale storage.
These problems are exacerbated by the natural structure of the land and human activities such as urbanization and agriculture. High levels of salts and arsenic are a health hazard, for which there is an urgent need for water purification and rainwater harvesting.
Urbanization and Industrial Effects on Underground Water in Punjab
Urban development and industrial activities in Punjab, Pakistan have negatively affected groundwater. Excessive water extraction, wastewater, and factory chemicals (iron, arsenic, bacteria) pollute the water. Hard roads and buildings prevent water from being absorbed into the ground, which is reducing water reserves and deepening the water table. Therefore, urgent planning for clean water and purification of factory water have become necessary.
Conclusion
The hydrological analysis of underground in Punjab Pakistan shows that groundwater is under serious stress. Over-extraction for agriculture, combined with urban and industrial growth, has lowered water tables, increased salinity, and caused contamination. Geological and climatic factors also influence recharge and water quality, making certain areas more vulnerable. Studies using ERS, GIS mapping, and groundwater modeling highlight these risks and identify zones where immediate attention is needed.
To protect Punjab’s underground water, sustainable management is essential. Solutions like managed aquifer recharge, pollution control, regular monitoring, and public awareness can help. Implementing these strategies ensures safe drinking water, supports agriculture, and secures long-term water resources for future generations, making the region more resilient to water scarcity.